
EAM Assessoria e Treinamentos no Processo Industrial e Segurança do Trabalho
Soluções de Problemas e Capacitação de Equipes

RH Plant
Some tips on Metallurgical Training
Do you know the meaning of Vacuum Degasser RH?
R is the short cut for Ruhrstahl
The first RH degasser was developed and installed at the steelmaking company Ruhrstahl AG, Germany.
H is the short cut for Heraeus.
Heraeus was a main supplier of vacuum pumps and constructed the vacuum pump for the first RH degasser.


Use of RH Degasser
-
Decarburization
-
Denitrogenation
-
Dehydrogenation
-
Maximum yield of oxygen-affine elements (e. g. B, Zr, Ti, V, Cr).
-
Control of small ranges of analyses.
-
Addition of large allying quantities (e. g. electrical sheets).
-
Treatment of steel grades with high demands on cleanness.
-
Light treatment.
Principles of RH Degassers
-
RH is a recirculation degassing process (continuous circulation of steel from the ladle via the inlet snorkel, lower RH vessel and outlet snorkel back to the ladle);
-
Inlet and outlet snorkel are immersed into the liquid steel by lifting of the steel ladle.
-
Inside the inlet snorkel lift gas nozzles (also called tuyeres) are installed;
-
Argon and nitrogen are used as lift gas types.
-
Lift gas stirring via the lift gas nozzles causes a partial quantity of the heat to be lifted into the RH vessel;
-
Re-circulation starts after app. 1/2 - 1 minute after opening of the vacuum flap;
-
A high turbulent steel flow the inlet to the outlet snorkel takes place;
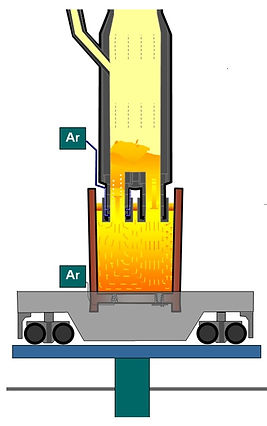
The fluid slow in the ladle is very smooth. Steel comes from the down leg snorkel back to the ladle, where its velocity is reduced;
The steel flows quite slowly to the bottom of the ladle and then turns back upward to the up leg snorkel, where the velocity will be increased again;
Re-circulation of molten steel is started;
Re-circulation rates are dependent on: Snorkel diameter, Lift gas flow rate and Vacuum pressure in the RH vessel.

Lift Gas Control
A constant lift gas flow rate during RH treatment has to be guaranteed.
Less lift gas flow rate can cause:
-
Clogging of lift gas nozzles.
-
Less steel re-circulation.
-
Less mixing and homogenisation of the steel in the ladle.
-
Less metallurgical reaction in the RH vessel itself.
For inner snorkel gunning and RH vessel deskulling the lift gas flow rate has to be increased in order to prevent lift gas nozzle clogging (~60-70 Nm³/h).

Checking work before ladle arrival
-
Steam conditions (inlet pressure, temperature).
-
Lift gas conditions (availability of nitrogen and argon, flow rate at line).
-
Cooling water conditions of open cooling water system (inlet pressure, flow rate, and temperature, outlet temperatures of condensers, pressure of hotwell pumps).
-
Cooling water conditions of closed cooling water system (inlet temperature, flow rate and pressure, outlet temperatures and pressure).
-
Vessel temperature.
-
Optional test of vacuum pump with closed vacuum flap.
Work before ladle take over to the ladle transfer car (if T-COB burner was in operation)
-
T-COB burner has to be switched off.
-
T-COB burner has to be in park position.
-
Gas cooler discharge flap drain has to be opened to drain condensed water generated from combustion of natural gas.
-
Gas cooler discharge flap has to be closed


Safe work and sequence before treatment in RH, as well as checking and general work after RH treatment are part of the content of our metallurgical training material, prepared for the training of professionals in the Secondary Refining area.
For metallurgical training, we have the necessary experience of the following content:
